India Leads Global Intangible Investment Revolution: Achieving 6.60% Growth Rate to Outperform USA, Greece, Czech Republic and Hungary
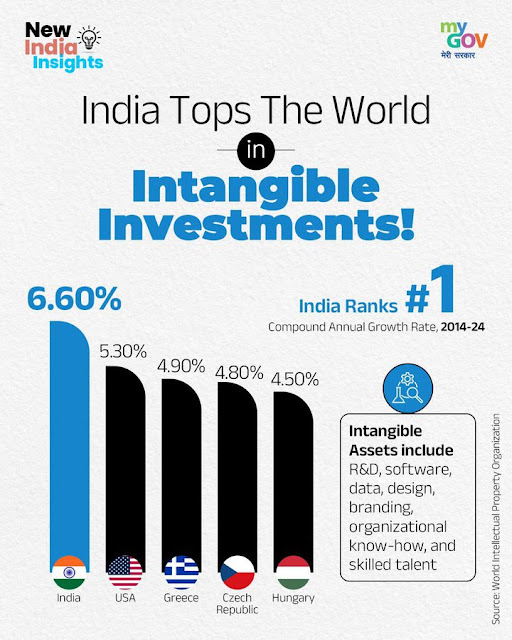
India has achieved an extraordinary milestone by becoming the global leader in intangible investments, recording an impressive compound annual growth rate of 6.60% between 2014-24, substantially outpacing major economies including the United States (5.30%), Greece (4.90%), Czech Republic (4.80%), and Hungary (4.50%). This remarkable achievement in intangible asset development signals India's successful transformation into a knowledge-driven economy, with strategic investments in research and development, software innovation, data analytics, design excellence, branding initiatives, organisational know-how, and skilled talent creating unprecedented value for the nation's economic future.
The significance of India's intangible investment leadership extends far beyond mere statistical achievement, representing a fundamental shift in the country's economic DNA towards knowledge-based value creation. This comprehensive analysis examines how India's strategic focus on intangible assets has positioned the nation at the forefront of the global innovation economy, creating sustainable competitive advantages that promise long-term prosperity and economic resilience in an increasingly knowledge-intensive world.
Understanding India's Intangible Investment Supremacy: The Knowledge Economy Foundation
India's ascendancy to the top position in global intangible investments represents a strategic economic transformation that has redefined the nation's competitive landscape. Intangible assets, encompassing research and development, software systems, data capabilities, design innovation, branding strength, organisational expertise, and skilled human capital, have become the primary drivers of India's economic growth and international competitiveness. This shift towards knowledge-based assets reflects India's recognition that sustainable economic development in the 21st century depends more on intellectual capital than physical infrastructure.
The World Intellectual Property Organisation's recognition of India's intangible investment leadership validates the country's strategic approach to building a knowledge economy. Unlike traditional economic models that emphasised manufacturing and physical asset accumulation, India's intangible investment strategy focuses on creating non-physical assets that generate long-term value through innovation, expertise, and intellectual property. This approach has enabled India to leapfrog traditional development stages and establish itself as a global leader in knowledge-intensive industries.
The comprehensive nature of India's intangible asset portfolio demonstrates the country's sophisticated understanding of modern economic drivers. By investing simultaneously in research and development capabilities, software innovation, data analytics, design excellence, branding initiatives, organisational know-how, and skilled talent development, India has created a robust ecosystem that supports sustained innovation and competitive advantage across multiple sectors.
This strategic focus on intangible investments has enabled India to achieve remarkable economic resilience and growth consistency, with the 6.60% compound annual growth rate reflecting the compound benefits of knowledge-based asset development. The multiplier effects of intangible investments create virtuous cycles of innovation, productivity improvement, and economic expansion that distinguish India's growth model from traditional resource-dependent economies.
Research and Development Excellence: India's Innovation Infrastructure Revolution
India's research and development sector has emerged as a cornerstone of the nation's intangible investment success, with both public and private sectors contributing to unprecedented levels of innovation activity. The country's R&D expenditure has grown exponentially, supported by government initiatives, private sector investments, and international collaborations that have created a comprehensive innovation ecosystem. This R&D focus has generated substantial intangible assets through patents, proprietary technologies, and scientific breakthroughs that enhance India's global competitiveness.
The pharmaceutical industry exemplifies India's R&D excellence, with companies investing heavily in drug discovery, biotechnology research, and clinical development programmes. Indian pharmaceutical firms have developed world-class research capabilities, creating valuable intangible assets through innovative drug formulations, manufacturing processes, and regulatory expertise. The sector's R&D investments have positioned India as both a global generic drug leader and an emerging player in innovative pharmaceutical development.
Information technology research and development has accelerated dramatically, with Indian companies and research institutions developing cutting-edge solutions in artificial intelligence, machine learning, blockchain technology, and quantum computing. These R&D initiatives have created substantial intangible asset value through proprietary algorithms, software platforms, and technological innovations that serve global markets. The IT sector's research investments have established India as a recognised leader in emerging technology development and implementation.
Government research institutions, including the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), and Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO), have contributed significantly to India's intangible asset development. These institutions have generated breakthrough innovations in space technology, defence systems, and scientific research that create substantial intellectual property value and enhance national technological capabilities.
Software Innovation and Digital Transformation: India's Technology Leadership
India's software development sector has become synonymous with global excellence, creating substantial intangible assets through innovative platforms, applications, and digital solutions that serve markets worldwide. The country's software industry has evolved from providing basic programming services to developing sophisticated enterprise solutions, consumer applications, and emerging technology platforms that generate significant intellectual property value and competitive advantages.
The digital transformation wave has amplified India's software innovation capabilities, with companies developing comprehensive solutions for cloud computing, enterprise software, mobile applications, and digital platforms. These software innovations represent substantial intangible assets through proprietary technologies, user databases, and market positioning that create sustainable competitive advantages. The sector's focus on emerging technologies has positioned India at the forefront of global digital transformation trends.
Fintech innovation has emerged as a particular strength of India's software sector, with companies developing revolutionary payment systems, digital banking platforms, and financial technology solutions that have transformed both domestic and international markets. The success of India's Unified Payments Interface (UPI) exemplifies the country's capability to develop world-class software solutions that create significant intangible asset value through widespread adoption and technological leadership.
The Indian government's Digital India initiative has accelerated software innovation across sectors, creating demand for digital solutions in healthcare, education, governance, and agriculture. This comprehensive digitalisation approach has generated opportunities for software companies to develop specialised solutions, building valuable intangible assets through domain expertise and technological capabilities that serve diverse market segments.
Data Analytics and Information Management: Building India's Data-Driven Economy
India's capabilities in data analytics and information management have emerged as critical components of the nation's intangible asset portfolio, with companies developing sophisticated systems for data collection, processing, analysis, and utilisation. The country's strength in data-related intangible assets stems from its large pool of skilled data scientists, advanced analytics infrastructure, and comprehensive understanding of data-driven business models that create competitive advantages across industries.
The financial services sector has leveraged data analytics to create substantial intangible asset value through risk assessment models, customer segmentation algorithms, and predictive analytics systems. Indian banks and financial institutions have developed proprietary data analytics capabilities that enhance operational efficiency, reduce risks, and improve customer experiences. These data analytics assets represent significant competitive advantages that support market leadership and profitability.
E-commerce and digital platform companies have built extensive data analytics capabilities that create substantial intangible asset value through customer insights, market intelligence, and personalisation algorithms. The ability to analyse vast amounts of consumer data and generate actionable insights has become a key differentiator for Indian companies operating in competitive digital markets.
Healthcare data analytics has emerged as a growing area of expertise, with Indian companies developing solutions for medical data analysis, drug discovery, and healthcare delivery optimisation. These healthcare analytics capabilities represent valuable intangible assets through proprietary algorithms, medical insights, and technological platforms that support improved patient outcomes and healthcare efficiency.
Design Innovation and Creative Excellence: India's Aesthetic and Functional Leadership
Design innovation has become an increasingly important component of India's intangible asset development, with companies and institutions investing significantly in design capabilities that enhance product functionality, user experience, and market appeal. India's design sector has evolved from traditional craftsmanship to encompass sophisticated industrial design, digital design, and user experience design that serves both domestic and international markets.
The automotive industry has been instrumental in developing India's design capabilities, with both domestic manufacturers and international companies establishing design centres in the country. These design facilities have created substantial intangible assets through innovative vehicle designs, manufacturing processes, and engineering solutions that serve global markets. The automotive design sector's growth has positioned India as a recognised centre for automotive innovation and design excellence.
Digital design and user experience have become critical areas of expertise for Indian companies, particularly in technology and e-commerce sectors. Indian designers and design firms have developed world-class capabilities in creating intuitive user interfaces, engaging digital experiences, and effective brand communications that enhance customer engagement and market positioning for clients across various industries.
The fashion and textile industry continues to contribute significantly to India's design-related intangible assets, with designers creating innovative products that combine traditional craftsmanship with contemporary aesthetics. This fusion of heritage and innovation has created unique design capabilities that are valued in global markets and contribute to India's cultural soft power and economic competitiveness.
Branding and Marketing Excellence: India's Global Brand Building Success
Brand development and marketing innovation have become essential components of India's intangible asset strategy, with companies investing substantially in building strong brand identities, customer relationships, and market positioning that create sustainable competitive advantages. India's branding capabilities have evolved from domestic market focus to encompass global brand building, with Indian companies successfully establishing international recognition and market presence.
The information technology services sector has achieved remarkable success in global brand building, with companies like Tata Consultancy Services, Infosys, and Wipro establishing strong international brands synonymous with quality, innovation, and reliability. These brand assets represent substantial intangible value through customer loyalty, premium pricing capabilities, and market recognition that support continued business growth and expansion into new markets.
Consumer goods companies have demonstrated exceptional brand building capabilities, with Indian brands achieving significant market share in categories including personal care, food and beverages, and household products. The success of brands like Patanjali, Amul, and Britannia demonstrates India's capability to create strong brand identities that resonate with consumers and create lasting market value through emotional connections and brand loyalty.
Digital marketing and social media expertise have become increasingly important components of India's branding capabilities, with companies developing sophisticated digital marketing strategies that leverage data analytics, content creation, and customer engagement platforms. These digital marketing capabilities represent valuable intangible assets that enhance brand visibility, customer acquisition, and market penetration across various demographic segments.
Organisational Know-How and Management Systems: India's Operational Excellence
Organisational capabilities and management systems constitute a crucial component of India's intangible asset portfolio, with companies developing sophisticated operational processes, management frameworks, and organisational structures that enhance efficiency, quality, and performance. India's strength in organisational know-how has been built through decades of experience managing complex operations, serving global clients, and delivering high-quality services across diverse industries.
The business process outsourcing sector has been instrumental in developing India's organisational capabilities, with companies creating world-class process management systems, quality frameworks, and operational excellence programmes that serve as global benchmarks. These organisational capabilities represent significant intangible assets through proprietary processes, management methodologies, and operational expertise that create competitive advantages and enable premium pricing.
Manufacturing industries have contributed substantially to India's organisational know-how through implementation of advanced manufacturing systems, quality management programmes, and operational excellence initiatives. The adoption of lean manufacturing principles, Six Sigma methodologies, and digital manufacturing technologies has created valuable intangible assets through improved operational capabilities and enhanced competitive positioning in global markets.
Project management and delivery excellence have emerged as distinctive strengths of Indian companies, particularly in sectors such as engineering, construction, and information technology. These project management capabilities represent valuable intangible assets through proven methodologies, execution frameworks, and delivery excellence that enable successful completion of complex projects and build strong client relationships.
Skilled Talent Development: India's Human Capital Revolution
Human capital development represents the most fundamental component of India's intangible asset portfolio, with the country demonstrating exceptional capabilities in developing skilled professionals across disciplines including technology, engineering, management, and research. India's emphasis on education, training, and skill development has created a substantial human capital base that supports innovation, productivity, and economic growth across multiple sectors.
The higher education system has been instrumental in developing India's skilled talent, with institutions like the Indian Institutes of Technology, Indian Institutes of Management, and various universities producing world-class graduates who contribute to intangible asset development. These educational institutions have created valuable intangible assets through research capabilities, knowledge creation, and talent development that support national competitiveness and innovation.
Professional development and training programmes have become increasingly sophisticated, with companies investing heavily in employee development, skill enhancement, and leadership training that builds organisational capabilities and competitive advantages. These training and development initiatives represent significant intangible assets through enhanced human capital, improved productivity, and innovation capabilities that drive business performance and market success.
The startup ecosystem has been supported by skilled talent across various domains, with entrepreneurs, technologists, and business professionals collaborating to create innovative solutions and build successful companies. This entrepreneurial talent represents valuable intangible assets through innovation capabilities, market knowledge, and business development expertise that contribute to economic growth and job creation.
Comparative Global Performance: India's Superior Investment Strategy
India's exceptional performance in intangible investments becomes more remarkable when compared to other major economies, with the country's 6.60% compound annual growth rate significantly exceeding the United States' 5.30%, demonstrating the effectiveness of India's focused approach to knowledge-based economic development. This performance differential highlights the strategic advantages of India's comprehensive intangible asset development strategy and the effectiveness of policy interventions supporting innovation and knowledge creation.
The United States, despite its advanced economy and substantial historical investment in research and development, has achieved a lower growth rate in intangible investments compared to India, suggesting that India's emerging economy dynamics combined with strategic focus are generating superior returns on knowledge-based investments. This comparative advantage demonstrates the potential for developing countries to achieve accelerated growth through strategic intangible asset development.
Greece's 4.90% performance in intangible investments, while solid, reflects the challenges faced by developed economies in maintaining high growth rates in knowledge-based assets. India's ability to substantially outperform Greece demonstrates the advantages of demographic dividends, educational investments, and innovation-friendly policies that support accelerated intangible asset development and knowledge economy growth.
The Czech Republic and Hungary, representing successful transition economies with 4.80% and 4.50% growth rates respectively, provide interesting comparison points for India's performance. India's superior results illustrate the potential for large emerging economies to leverage scale advantages, diverse talent pools, and comprehensive policy frameworks to achieve exceptional results in knowledge-based economic development.
Economic Impact and Value Creation: Quantifying India's Success
The economic impact of India's intangible investment leadership extends far beyond direct financial returns, with these knowledge-based assets contributing substantially to GDP growth, productivity improvements, and overall economic competitiveness. Intangible assets have become primary drivers of economic value creation, with studies indicating that intangible investments contribute significantly to national wealth accumulation and long-term economic prosperity.
Productivity improvements across sectors have resulted from India's focus on intangible asset development, with companies leveraging research and development, software capabilities, and organisational excellence to enhance efficiency and create value. These productivity gains translate directly into economic benefits through increased output, higher profitability, and enhanced competitiveness in global markets that support continued economic growth.
The multiplier effects of intangible investments are particularly significant in India's economic context, with knowledge-based assets generating spillover benefits across industries and regions. Software development capabilities create digital transformation opportunities across sectors, while research and development investments generate innovations that benefit multiple industries and contribute to overall economic advancement.
Export performance has been substantially enhanced by India's intangible asset development, with competitive advantages in software services, research and development, and skilled talent enabling significant export growth in knowledge-intensive sectors. These export capabilities represent successful monetisation of intangible assets in global markets, contributing to foreign exchange earnings and economic stability.
Policy Framework and Government Support: Enabling India's Success
The Indian government has implemented a comprehensive policy framework supporting intangible asset development through various initiatives, incentives, and programmes designed to enhance research and development, promote innovation, and build human capital. These policy interventions have been instrumental in creating an enabling environment for intangible investment growth and positioning India as a global leader in knowledge-based economic development.
The National Innovation Policy and science and technology missions have provided strategic direction for intangible asset development, establishing priorities, allocating resources, and creating institutional frameworks that support innovation and research activities. These policy initiatives have facilitated collaboration between government, industry, and academic institutions, maximising the impact of intangible investments and accelerating knowledge creation.
Intellectual property protection and enforcement have been strengthened through legal and regulatory reforms, providing greater security for intangible assets and encouraging continued investment in research and development, software development, and innovation activities. These intellectual property protections enhance intangible asset value and provide incentives for continued investment in knowledge-based activities.
Tax incentives and financial support mechanisms have been implemented to encourage intangible asset development, with programmes including weighted deduction for research and development expenditure, software development incentives, and startup support schemes. These financial incentives have reduced the cost of intangible asset development and encouraged greater private sector participation in knowledge-based activities.
Industry Sector Contributions: Driving India's Leadership
The pharmaceutical industry has emerged as a major contributor to India's intangible asset portfolio, with companies investing heavily in drug discovery, clinical research, and biotechnology development. Indian pharmaceutical companies have developed substantial research and development capabilities, creating valuable intangible assets through patents, proprietary technologies, and regulatory expertise that support global competitiveness and market expansion.
Information technology services continue to dominate India's intangible asset development, with companies creating sophisticated software solutions, digital platforms, and technology services that serve clients worldwide. The IT sector's investment in research and development, intellectual property creation, and talent development has generated substantial intangible asset value that supports India's position as a global technology leader.
The automotive industry has contributed significantly to India's intangible assets through design innovation, manufacturing excellence, and technology development. Both domestic and international automotive companies have established research and development centres in India, creating valuable intangible assets through product design, process innovation, and engineering capabilities that serve global markets.
Financial services have demonstrated exceptional capabilities in developing intangible assets through fintech innovation, digital banking platforms, and financial technology solutions. The sector's investment in technology development, data analytics, and customer experience innovation has created substantial intangible asset value that supports market leadership and competitive positioning.
Future Prospects and Strategic Opportunities: Sustaining Leadership
The future prospects for India's intangible investment leadership appear exceptionally promising, with several strategic opportunities emerging that could further strengthen the country's position in knowledge-based economic development. The continued growth of digital technologies, artificial intelligence, and data analytics creates opportunities for India to build additional intangible assets and expand competitive advantages in emerging technology areas.
The development of India's startup ecosystem presents significant opportunities for intangible asset creation, with entrepreneurs and innovators developing new technologies, business models, and solutions that create intellectual property and competitive advantages. Government support for startup development, combined with increasing venture capital availability, provides a conducive environment for continued intangible asset growth and innovation.
International collaboration and partnerships offer additional opportunities for intangible asset development, with India's established capabilities in research and development, software development, and skilled talent making the country an attractive partner for global innovation initiatives. These collaborations can accelerate knowledge transfer, technology development, and capability building that enhance India's intangible asset portfolio.
The integration of emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, blockchain, and quantum computing into India's innovation ecosystem presents opportunities to develop next-generation intangible assets that could provide competitive advantages in future market segments. Strategic investments in these technologies could position India as a leader in the next wave of technological innovation.
Challenges and Risk Management: Maintaining Competitive Edge
Despite India's exceptional performance in intangible investments, several challenges need to be addressed to maintain and strengthen the country's leadership position. Intellectual property protection remains a critical concern, with the need for continued strengthening of legal frameworks, enforcement mechanisms, and international cooperation to safeguard India's growing intangible asset portfolio from unauthorised use and infringement.
Talent retention and brain drain represent ongoing challenges that could impact India's intangible asset development capabilities. The country needs to create attractive career opportunities, competitive compensation packages, and innovation-friendly environments that retain skilled professionals and encourage continued knowledge creation and innovation activities within India's borders.
Infrastructure development remains crucial for supporting intangible asset creation, with continued investments needed in research facilities, technology infrastructure, and digital connectivity that enable efficient knowledge creation and dissemination. These infrastructure investments are essential for maintaining India's competitive advantages in knowledge-intensive sectors and supporting continued growth.
International competition is intensifying as other countries recognise the importance of intangible assets for economic development. India needs to continue innovating in its approaches to intangible asset development, maintaining its competitive edge through strategic investments, policy innovations, and international collaboration that sustain its leadership position in the global knowledge economy.
Conclusion: India's Intangible Investment Model for Global Development
India's achievement in becoming the global leader in intangible investments, with an exceptional 6.60% compound annual growth rate, represents a fundamental transformation of the country's economic structure and competitive positioning that provides valuable lessons for global economic development. This leadership in knowledge-based asset development demonstrates India's successful transition from a resource-dependent economy to a knowledge-driven economy that creates value through innovation, expertise, and intellectual capital.
The comprehensive nature of India's intangible asset portfolio, encompassing research and development, software development, data analytics, design innovation, branding, organisational know-how, and skilled talent, provides a robust foundation for sustained economic growth and competitive advantage. This diversified approach to intangible asset development reduces economic risks and creates multiple sources of value creation that support long-term prosperity and resilience.
The policy framework, industry initiatives, and strategic investments that have driven India's intangible investment success provide a replicable model for other developing countries seeking to build knowledge-based economies. The Indian experience demonstrates that focused investment in education, research and development, technology development, and innovation ecosystem building can generate exceptional returns in terms of economic growth and global competitiveness.
As India continues to build on its intangible investment leadership, the country is exceptionally well-positioned to maintain its competitive advantages and expand its influence in the global knowledge economy. The foundation of intangible assets created over the past decade provides a strong platform for future growth, innovation, and economic development that will benefit not only India but also contribute to global prosperity through knowledge sharing, technology transfer, and collaborative innovation initiatives that advance human progress and economic development worldwide.
---------------------------------------------------------------
"This Content Sponsored by Buymote Shopping app
BuyMote E-Shopping Application is One of the Online Shopping App
Now Available on Play Store & App Store (Buymote E-Shopping)
Click Below Link and Install Application: https://buymote.shop/links/0f5993744a9213079a6b53e8
Sponsor Content: #buymote #buymoteeshopping #buymoteonline #buymoteshopping #buymoteapplication"